BRING NATURE HOME
Make your house a home with natural sustainable eco friendly products. Discover handmade ethical products.
Shop NowOur collections
Featured collection
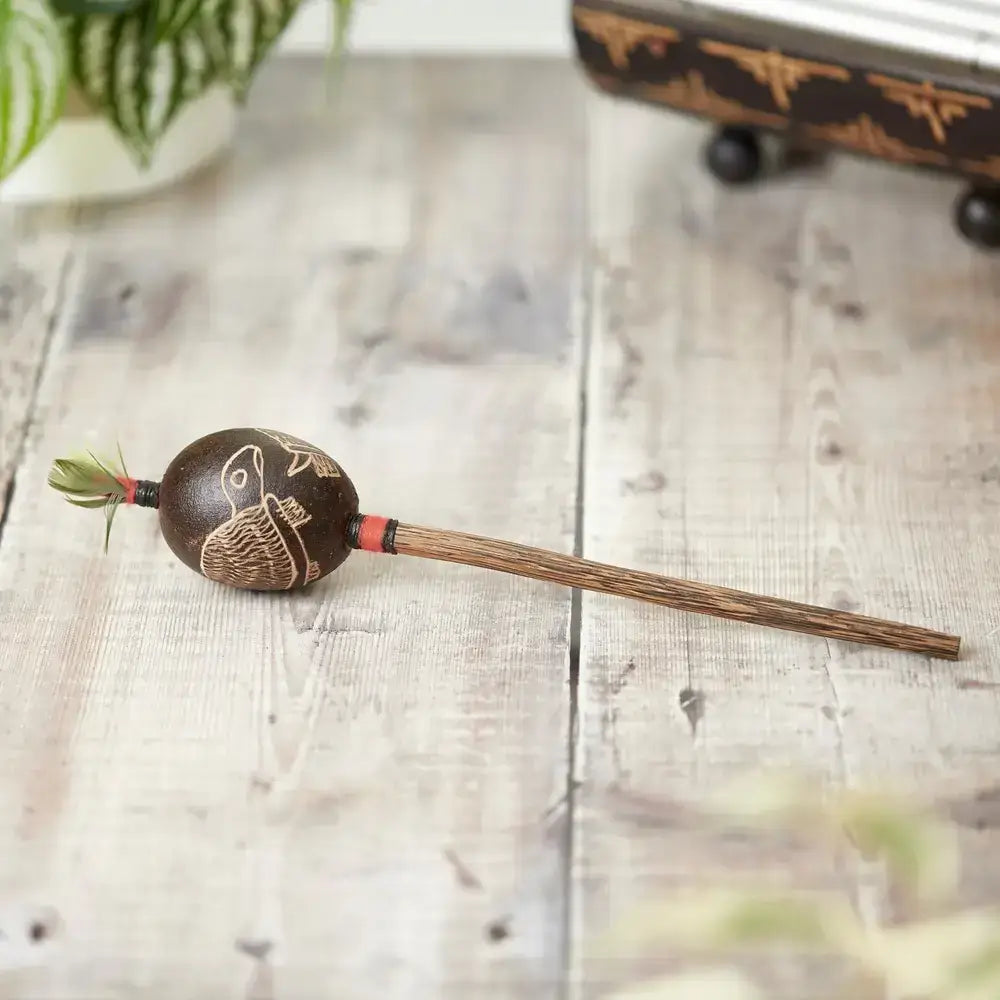

Peruvian Shipibo Shaker
Sale priceFrom £20.00
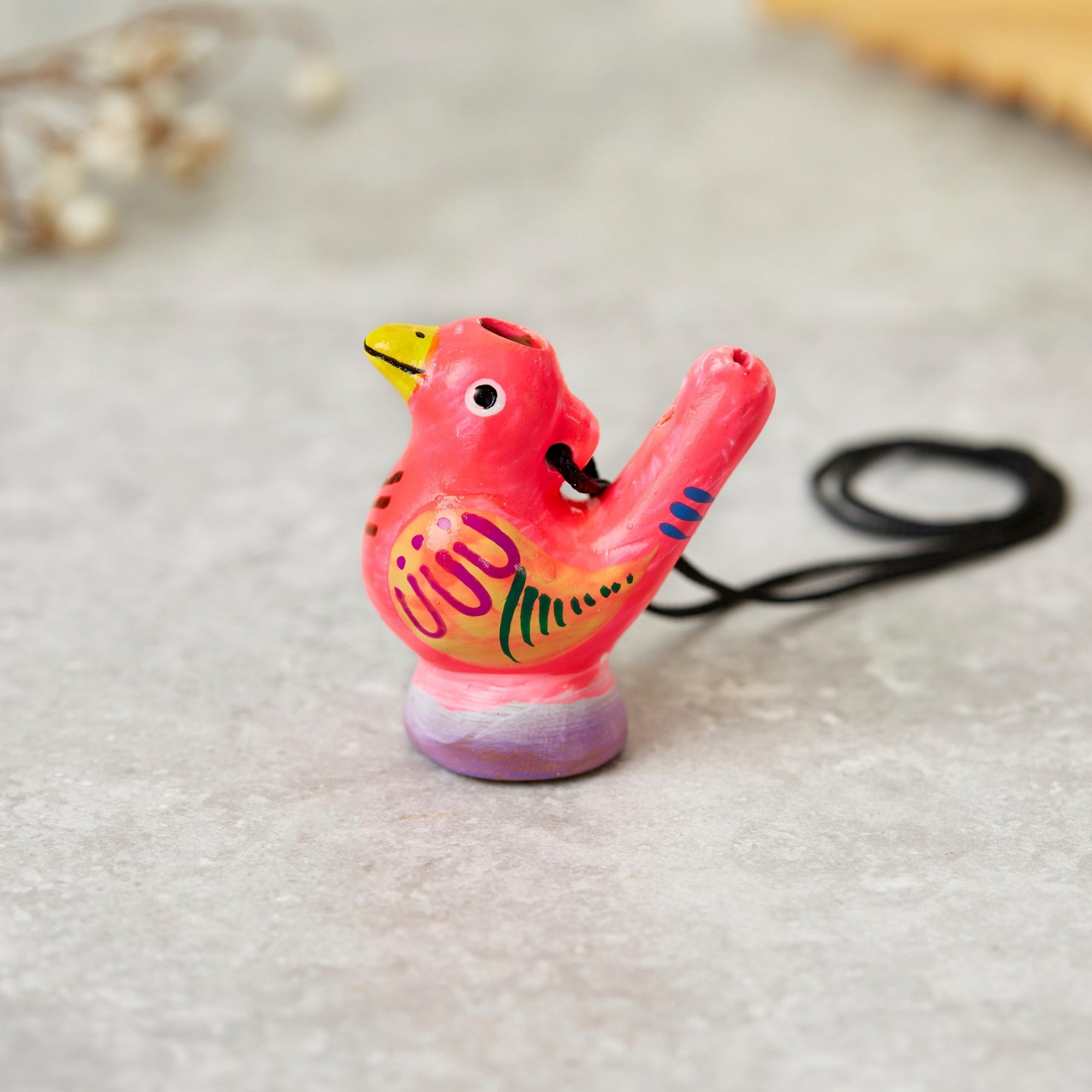

Peruvian Bird Water Whistle
Sale priceFrom £15.00
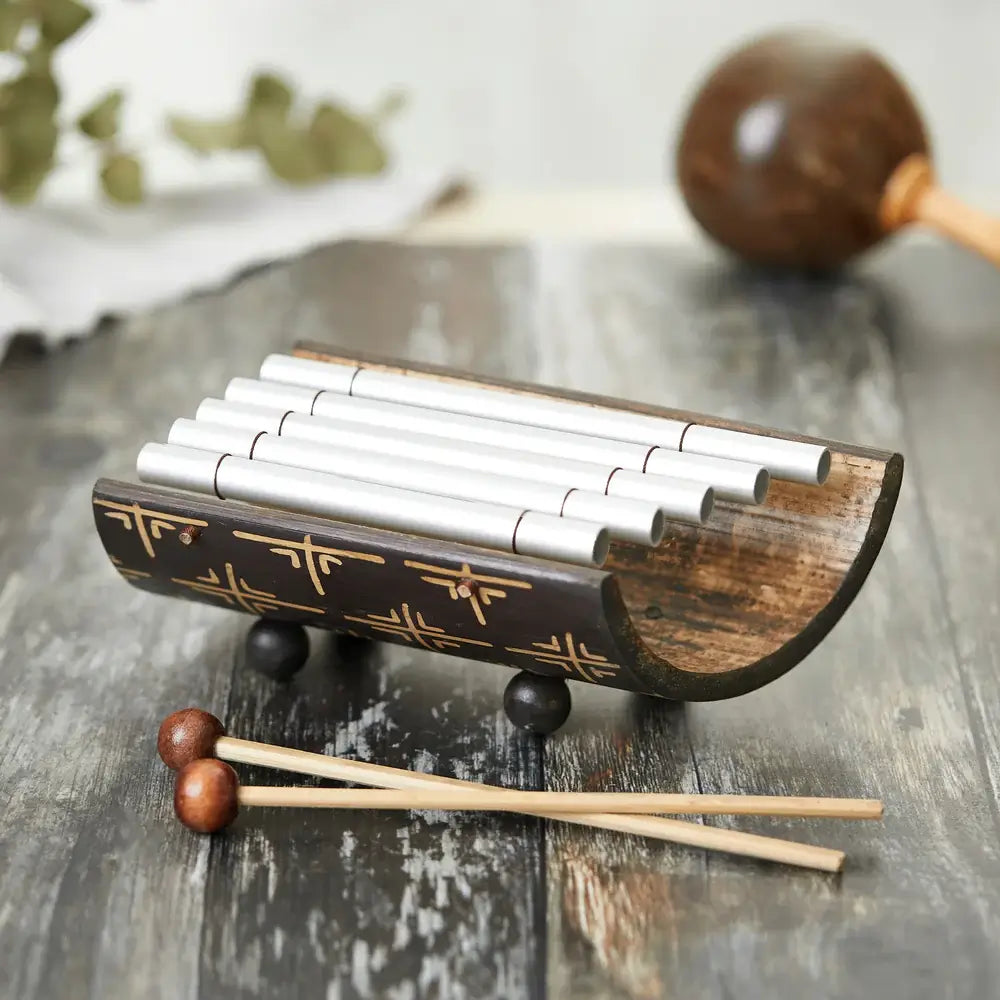

Gamelan Xylophone
Sale price£25.00
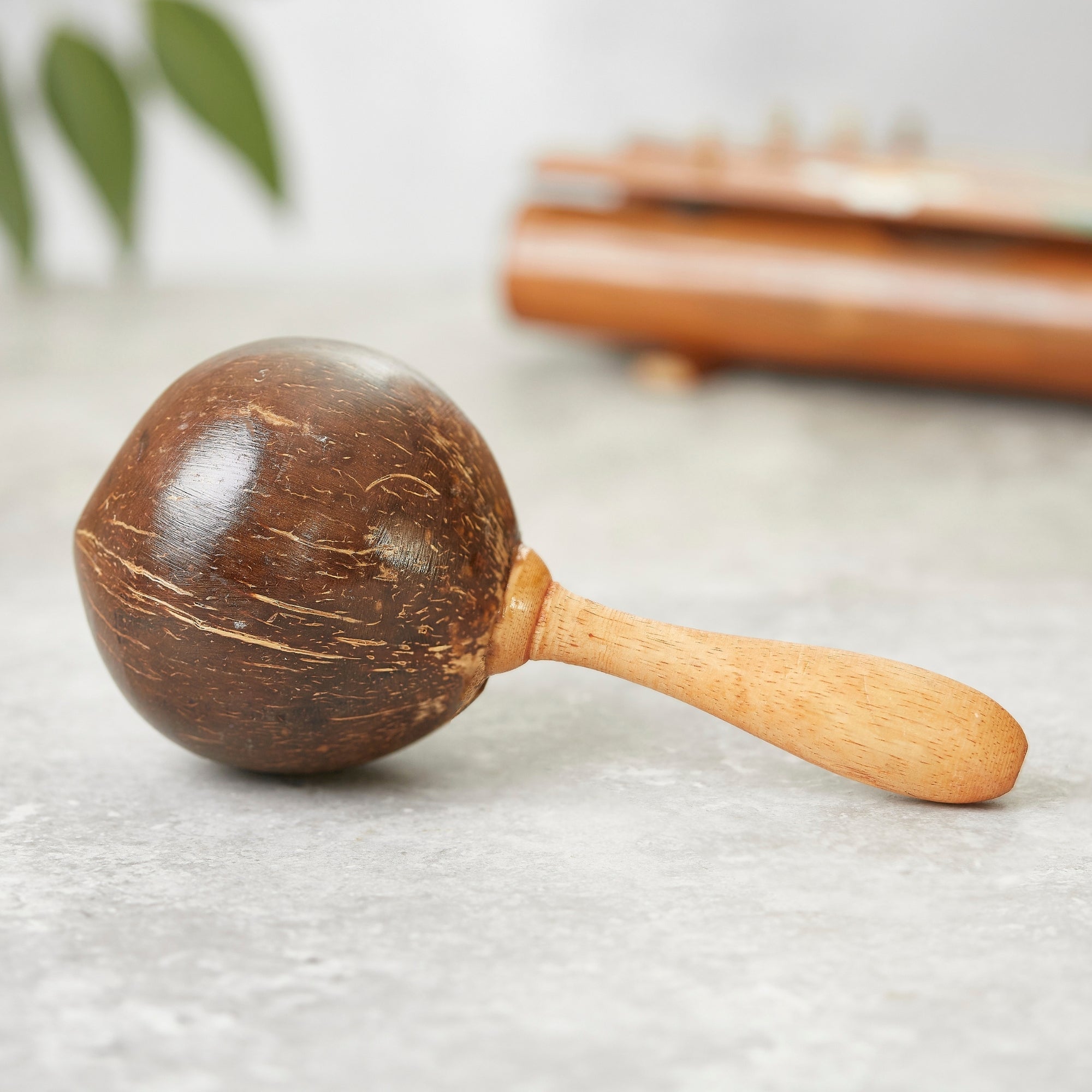

Coconut Shell Maraca
Sale price£15.00
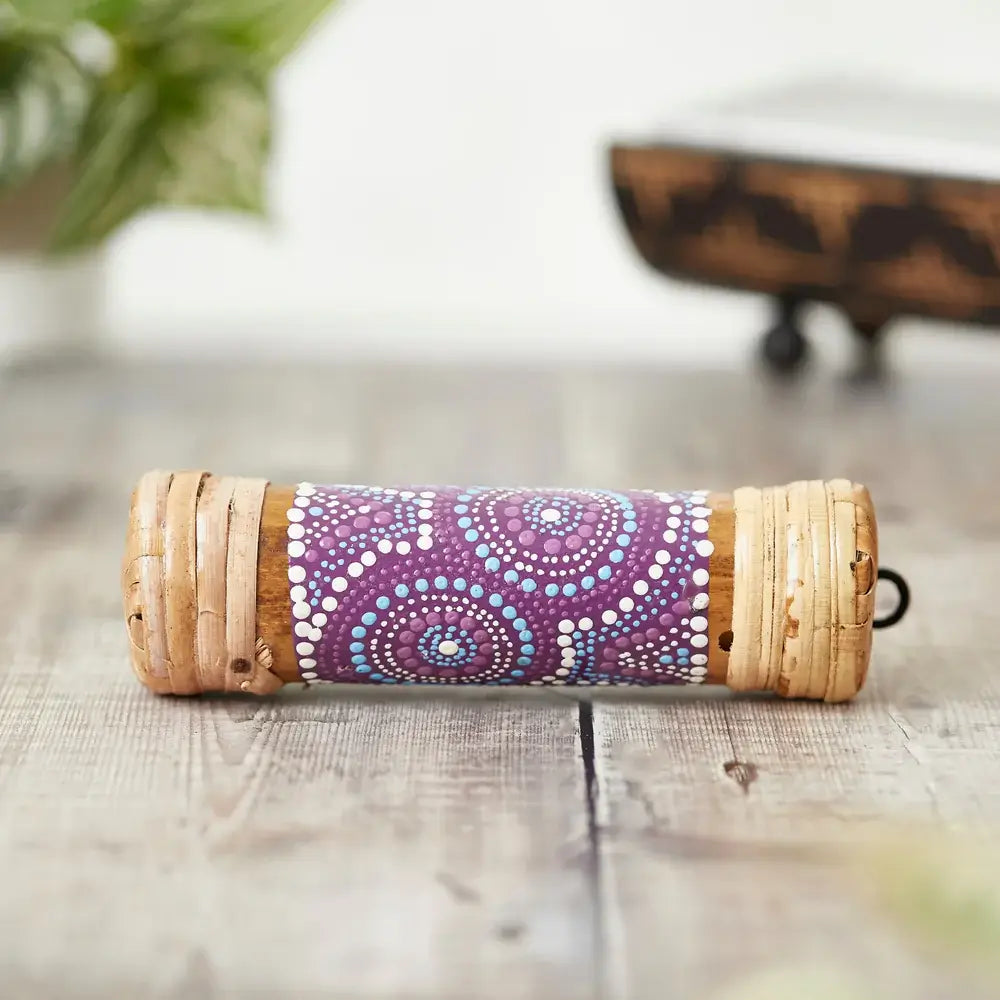

Painted Bamboo Rainstick
Sale priceFrom £15.00
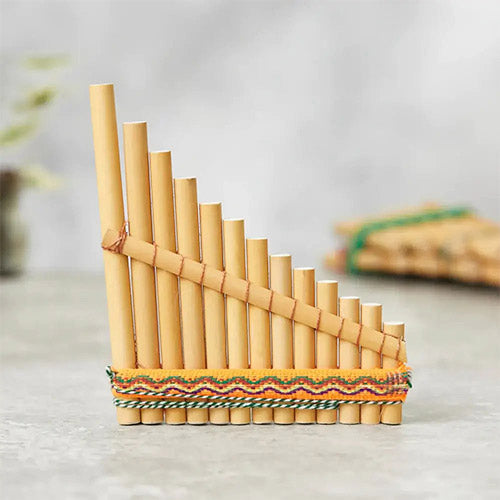

Antares Bamboo Pan Pipes
Sale price£15.00
New Arrivals
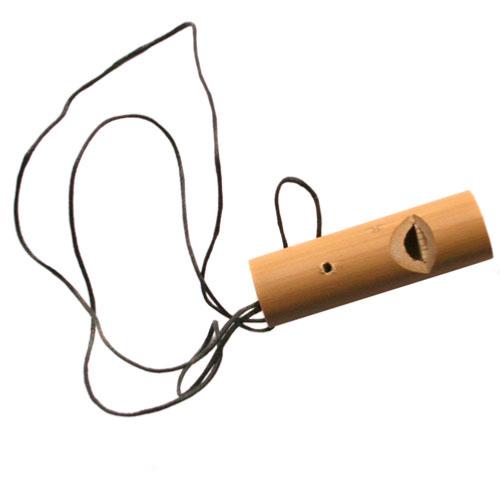

Jambi Bamboo Whistle
Sale price£12.00
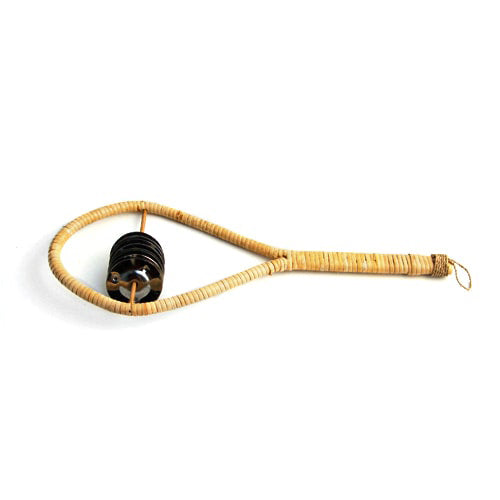

Sawan Rakatak
Sale price£15.00
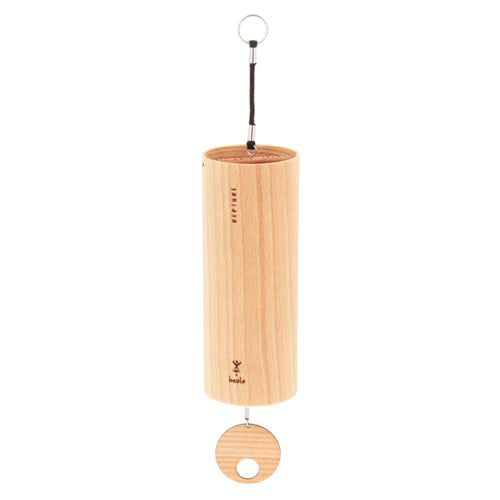

Heola Windchime – Neptune
Sale price£55.00
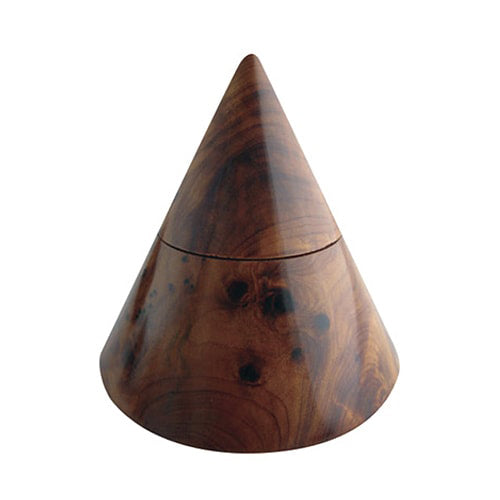

Thuya Conical Box
Sale price£20.00

Fidget Snake
Sale price£15.00

Finger Trap
Sale price£10.00
Discover Carved Culture
We work with artisans around the world to create handmade products for the home. Each unique design is made from natural materials or with the environment in mind.
Our Journal
We are always working to provide more value to you, from the products that we sell, the articles we write, to the videos that we make. We believe education should be free, which is why we share craft ideas, and food recipes from around the world.
View our Blog
Brian Eno - An Ending (Ascent) (Kalimba Tab)
"An Ending (Ascent)" by Brian Eno is an ambient instrumental track that embodies a sense of tranquility, introspection, and transcendence. The song...

What is a sound profile?
Our sound profiles are in technical terms a way to precisely describe the sound of each of our musical instruments. They go beyond mere description...

Bon Jovi - Always (Kalimba Tab)
"Always" by Bon Jovi is a power ballad that speaks about the enduring nature of love despite challenges and hardships. The lyrics depict a person w...